I. The PC or operating system is faulty.
II. The environment has problems (such as loops or attacks).
III. The physical link is disconnected.
IV. The device configurations are in corrector improper, mainly including:
The DHCP Snooping trust interface is incorrect configured.
The VLAN allocation on the switch is incorrect and the IP address of the layer-3 interface is not configured on the DHCP server.
The relay function is not enabled on the layer-3 interface.
No IP address pool is configured on the DHCP server or the IP address pool is configured with excluded addresses, which causes that no available IP addresses in the IP address pool.
The lease time configured for the DHCP server is too long, and no IP addresses can be released.
The network segment configuration for the IP address pool of the DHCP server is incorrect.
The switches are not enabled with DHCP.
V. The performance of the DHCP server is inadequate.
VI. The software version has defects.
VII. The DHCP architecture is incorrect:
When the DHCP relay and DHCP Snooping are deployed on the network of the customer, the enabling positions are improper, which causes that the client cannot obtain DHCP normally.
Cause: The DHCP relay will modify the source MAC address (modify to the MAC address of the DHCP relay) of a DHCP packet sent by the PC. If the DHCP relay is deployed before DHCP snooping device, the DHCP packet will be discarded by the snooping device.
Correct architecture deployment:
(1) Deploy the DHCP Snooping and DHCP relay function on the same device, e.g., PC-Device (deploy DHCP Snooping and DHCP Relay simultaneously)–Device (deploy DHCP Server).
(2) Deploy the DHCP Snooping on the downlink device of the DHCP relay, e.g., PC-Device (deploy DHCP Snooping)-Device (deploy DHCP Relay)-Device (deploy DHCP Server).
I. Check the client and operating system.
II. Check the network environment.
III. Check whether the network device configurations are correct.
IV. Check whether the performance of the DHCP server is adequate.
V. Check the software versions of network devices.
VI. Collect information and contact ruijie post-sale for help.
Step 1: Check the client and operating system.
(1) Identify the fault symptom and check whether the client is configured to dynamically obtain IP addresses as shown in the following picture.
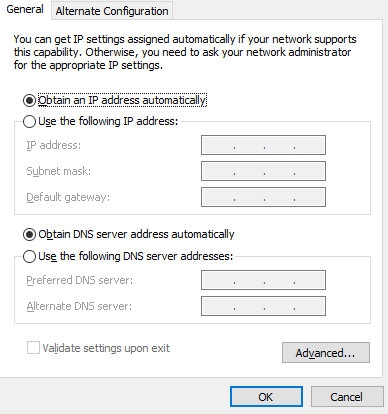
(2) Check whether a single client or many clients fail to obtain IP addresses automatically. If many clients fail to obtain IP addresses, go to the next step.
If this fault occurs only on a single client, you can install packet capturing software on the PC, or perform mirroring and packet capturing on the access switch to check whether the PC sends DHCP discover packets normally.
If not, you can attempt to disable and then enable the network interface card. For a diskless system, it is recommended to make a diskless server system.
If DHCP discover packets can be normally sent, retain the packets captured and go to the next step.
Step 2: Check the network environment.
(1) Check whether the physical link between the client and server is normal.
Configure the PC to use a static IP address and gateway. If you are sure that the switch is not configured with the IP source-guard function, ping the IP address of the server to check the connection. If the IP address can be successfully pinged, the delay is smaller than 100ms, and no packet loss or jitter occurs, it indicates that the connection is normal, namely, the physical link is not faulty. Go to the next step for fault locating. If the IP address fails to be pinged, the delay is large, or packet loss occurs, it indicates that the physical link is faulty or the server is unstable due to environment problems. In this case, you need to perform packet capturing from the client to the DHCP server node by node to identify the cause for the packet loss or large delay.
(2) Check whether the link is disconnected. If yes, correctly connect the interfaces. Check whether the route of the devices is correct. If not, adjust the route.
If the fault persists, check whether the CPU usages of the switches along the route are high, especially when a device is used as the DHCP server. If the CPU usage of a switch is high, locate the cause by using <<>>.
If the fault still persists, go to the next step.
Step 3: Check whether the configurations of network device are correct.
In a DHCP network, devices are classified into the DHCP relay, DHCP server and DHCP Snooping. DHCP Snooping ensures DHCP security and prevents static IP configuration, which can be used together with DAI to prevent ARP spoofing. A device may have one or more roles in the network(for example, a device can be configured as DHCP server and DHCP snooping simultaneously). Check whether the basic configurations are correct by using the following methods:
Login to an access switch through the Console port, and then run the show run command to display the configurations.
全部评论